3841. Dr Who’s Banquet
Dr. Who is
organizing a banquet and will be inviting several guests. A guest is happy if
he can chat with a fixed number of other guests. We assume that guests cannot
talk to themselves. Help Dr. Who make all his guests happy, if possible, by
organizing chats between guests.
Input. Contains several data sets, and each data
set is encoded on a line. A data set consists of n (n ≤ 10000) positive
integers a1, a2, … an. Each number ai (ai ≤ 1000, 1 ≤ i ≤ n) is the number of
chat partners guest i would like
to have.
Output. If you can make all the guests happy, you
should post “ok”. If not all the guests to be happy, you should get the message
“fail”. After each message should be displayed an empty string.
In the following
table, an input data with 4 data sets and the associated output is
shown.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
3 3 1 1 4 4 3 3 2 2
2 3 3 1 1 2 2 2 2 |
fail ok fail ok |
SOLUTION
priority queue
Algorithm analysis
Example
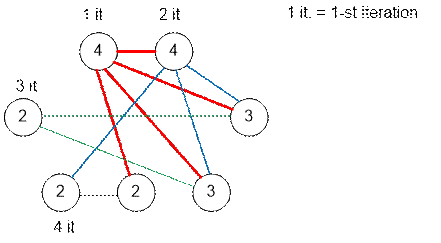
In the fourth test, there are 4 guests, each wants to communicate
with two others. Communication partners can be set up as follows:
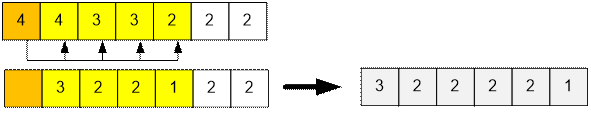
Let’s consider the second test. There are 7 guests in total. For
communication with a person who wants to have 4 interlocutors, we will assign
those who want to have 4, 3, 3 and 2 interlocutors, respectively.
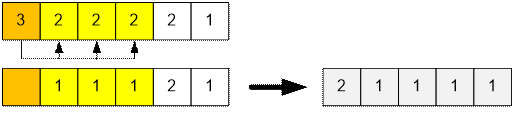
For communication with a person who wants to have 3 more
interlocutors, we will assign those who want to have 2, 2 and 2 interlocutors,
respectively.
Third iteration:
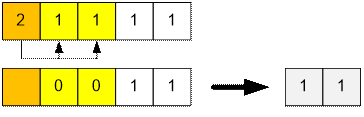
Fourth (last) iteration:
Algorithm realization
Declare a max-priority queue.
priority_queue<int> pq;
Queue processing according to the above described algorithm.
bool process(priority_queue<int>
&q)
{
while(!q.empty())
{
Extract a guest who wants to have v
interlocutors. The value
v is the maximum in the queue.
int v = q.top(); q.pop();
queue<int> add;
The guest should find exactly v interlocutors, make v
iterations.
while(v--)
{
If the queue is empty, then all
interlocutors will not be found, the answer will be fail.
if (q.empty()) return
false;
Decrease the number of interlocutors for the next guest by 1. The number
of desired interlocutors for the next guest is stored in add queue.
if (q.top() != 1) add.push(q.top() - 1);
q.pop();
}
Return the interlocutors from the add queue to q.
while(!add.empty())
{
q.push(add.front());
add.pop();
}
}
return true;
}
The main part of the program. Read the numbers of one line (one test).
When the ‘\n’ character is
read after the number, the data will be processed. If the answer is positive, then print ok, otherwise print fail.
while(scanf("%d%c",&n,&c)
== 2)
{
pq.push(n);
if (c == '\n')
{
printf(process(pq) ? "ok\n\n"
: "fail\n\n");
Clean up the queue for the next test case.
while(!pq.empty()) pq.pop();
}
}